Autonomous delivery vehicles (ADVs) are rapidly transforming the way goods are transported. No longer a distant vision of the future, self-driving delivery vehicles are actively being deployed and tested across urban and suburban areas worldwide. From grocery orders to medical supplies, these vehicles promise faster deliveries, reduced operational costs, and improved safety for both drivers and pedestrians. This article examines the rise of autonomous delivery vehicles, emerging trends, technological advancements, regulatory developments, and their potential impact on businesses and consumers.
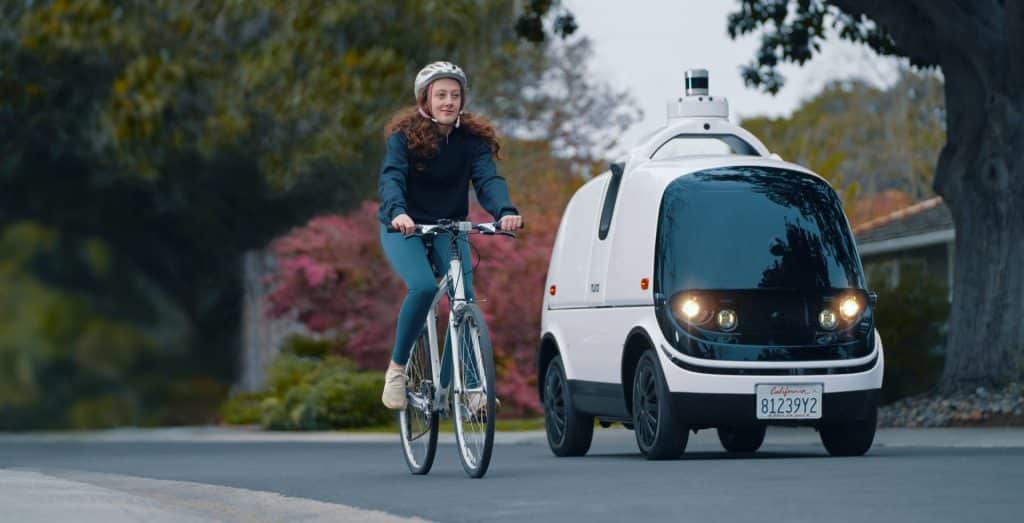

What Are Autonomous Delivery Vehicles?
Autonomous delivery vehicles are self-driving cars, vans, or small robots designed to transport goods without a human driver. Leveraging artificial intelligence, sensors, and advanced navigation systems, ADVs can safely maneuver through complex environments. Companies like Amazon, FedEx, Nuro, and Starship Technologies are at the forefront of this technology, experimenting with both large and small-scale deployments.
Key advantages of autonomous delivery vehicles include:
- Faster deliveries: ADVs can operate around the clock without fatigue, reducing delays caused by human drivers.
- Cost savings: Labor, fuel, and operational expenses can be significantly reduced over time.
- Environmental benefits: Many autonomous delivery vehicles are electric, reducing emissions from traditional delivery trucks.
- Enhanced customer experience: Real-time tracking and contactless delivery improve convenience and safety for consumers.
In 2023, Nuro’s autonomous delivery robots were operating in multiple U.S. cities, successfully delivering groceries and other essentials directly to customers’ doorsteps (TechCrunch, 2023).
Emerging Trends in Autonomous Delivery
Autonomous delivery vehicles are no longer experimental. Several trends are emerging that indicate widespread adoption is imminent.
1. Expansion of Urban Robot Delivery
Urban areas are ideal environments for small autonomous delivery robots. These compact machines can navigate sidewalks, pedestrian paths, and low-traffic streets to deliver food, groceries, and small packages. Current developments include:
- AI-powered navigation systems that detect pedestrians, pets, and obstacles.
- Contactless delivery lockers integrated with smart technology.
- Collaborative initiatives with local businesses to optimize last-mile delivery.
According to Grand View Research (2023), the global autonomous delivery robot market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% between 2025 and 2030, indicating strong investor and consumer confidence.
2. Integration with E-Commerce Platforms
E-commerce companies are driving the adoption of autonomous delivery vehicles by integrating them into their logistics networks. Amazon has tested autonomous delivery vans in select U.S. regions, while Walmart explores self-driving grocery delivery services.
Benefits of this integration include:
- Faster deliveries: Ensures same-day or even within-the-hour delivery for consumers.
- Operational efficiency: Reduces dependency on human couriers, especially during peak seasons.
- Enhanced analytics: Collects valuable data on consumer behavior and delivery efficiency.
By seamlessly integrating ADVs into their supply chains, e-commerce companies aim to improve delivery reliability and customer satisfaction while cutting costs.
3. Regulatory Developments and Safety Standards
For autonomous delivery vehicles to operate safely in public spaces, governments and regulatory bodies are gradually establishing legal frameworks. The U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has published guidelines to ensure safety and transparency during testing on public roads (NHTSA, 2023).
Key regulatory trends include:
- Safety testing requirements prior to public deployment.
- Standardized vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication systems.
- Local permits for operating delivery robots on streets and sidewalks.
Such regulations are crucial to ensure ADVs are deployed responsibly, gaining public trust and avoiding operational risks.
4. Technological Innovations Driving Efficiency
Autonomous delivery vehicles rely on cutting-edge technologies to operate safely and efficiently. Core components include:
- Lidar and computer vision: For real-time obstacle detection and accurate navigation.
- Artificial intelligence: Optimizes delivery routes, reduces energy consumption, and adapts to dynamic urban environments.
- Fleet management software: Enables companies to monitor and coordinate multiple vehicles simultaneously.
Recent innovations also focus on battery longevity and load capacity, allowing ADVs to carry heavier payloads and serve more diverse delivery needs. These advancements make autonomous delivery vehicles viable for both small-scale food deliveries and larger retail shipments.
5. Consumer Acceptance and Adoption
Public perception is a critical factor in the success of autonomous delivery. Surveys indicate that while initial consumer skepticism exists, trust grows when delivery services are reliable, safe, and convenient. Companies are responding by:
- Offering transparent safety demonstrations.
- Providing real-time tracking for every delivery.
- Introducing insurance and liability coverage for autonomous deliveries.
As ADVs become more common, consumer confidence is expected to rise, further accelerating adoption rates.
Business Impacts of Autonomous Delivery Vehicles
The rise of ADVs presents numerous economic opportunities and challenges for businesses. Key implications include:
- Cost reduction: Last-mile delivery is one of the most expensive components of logistics. Autonomous delivery vehicles can reduce labor and fuel costs by 30-50%.
- Job transformation: While traditional delivery jobs may decline, new roles in fleet monitoring, AI system management, and maintenance will emerge.
- Market growth: The autonomous delivery vehicle market is projected to exceed $30 billion by 2030 (McKinsey, 2023).
By adopting autonomous delivery technology early, companies can gain a competitive edge, improve operational efficiency, and enhance customer loyalty.
Overcoming Challenges and Limitations
Despite promising benefits, autonomous delivery vehicles face several hurdles:
- Infrastructure: Urban environments require redesigned roads, sidewalks, and smart traffic management systems to accommodate ADVs.
- Technical reliability: Sensors and AI systems must operate flawlessly under diverse weather conditions, including rain, snow, and extreme heat.
- Cybersecurity: Autonomous systems must be safeguarded against hacking, data breaches, and operational manipulation.
- Public perception: Continuous education and transparency are necessary to alleviate consumer skepticism and build trust.
Addressing these challenges is critical for mainstream adoption and long-term viability.
The Environmental Advantage
Autonomous delivery vehicles also contribute to sustainability. Many ADVs are electric, reducing greenhouse gas emissions from traditional delivery trucks. Furthermore:
- Optimized routing reduces unnecessary driving distances.
- Small delivery robots have minimal energy consumption compared to larger vehicles.
- ADVs can support carbon-neutral delivery initiatives, which are increasingly demanded by eco-conscious consumers.
These factors make autonomous delivery vehicles attractive not only for cost savings but also for companies seeking to meet environmental goals.
Global Trends and Case Studies
Several countries and companies are actively piloting autonomous delivery programs:
- United States: FedEx and UPS are testing autonomous vans in suburban areas. Nuro operates grocery delivery robots in multiple cities.
- Europe: Starship Technologies deploys small sidewalk robots for food and parcel deliveries in cities like London and Berlin.
- Asia: In Japan and South Korea, autonomous delivery vehicles are being integrated into urban logistics to manage densely populated city centers.
These case studies demonstrate the versatility and growing adoption of ADVs across different urban environments, suggesting that the technology is scalable and adaptable worldwide.
The Future of Delivery
The rise of autonomous delivery vehicles is set to redefine logistics. Over the next decade, we can expect:
- Expanded deployment in urban, suburban, and even rural areas.
- Collaboration between retailers, technology firms, and logistics providers to optimize delivery efficiency.
- Increased consumer expectations for fast, reliable, and environmentally friendly delivery services.
Businesses that embrace autonomous delivery early will not only improve operational efficiency but also shape customer experience, setting a new standard for convenience and reliability in the logistics sector.
References
- TechCrunch. “Nuro Expands Autonomous Grocery Delivery Service.” Available at: https://techcrunch.com (Accessed: 21 August 2025).
- Grand View Research. “Autonomous Delivery Robot Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report.” Available at: https://www.grandviewresearch.com (Accessed: 21 August 2025).
- NHTSA. “Automated Vehicles for Safety.” Available at: https://www.nhtsa.gov (Accessed: 21 August 2025).